Concepts for new switchable plasmonic nanodivices
A magneto-plasmonic nanoscale router and a high-contrast magneto-plasmonic disk modulator controlled by external magnetic fields
Plasmonic waveguides open the possibility to develop dramatically miniaturized optical devices and provide a promising route towards the next-generation of integrated nanophotonic circuits for information processing, optical computing and others. Key elements of nanophotonic circuits are switchable plasmonic routers and plasmonic modulators. Recently Dr. Joachim Herrmann (MBI) and his external collaborators developed new concepts for the realization of such nanodevices. They investigated the propagation of surface-plasmon-polaritons (SPP) in magneto-plasmonic waveguides. Based on the results of this study they proposed new variants of switchable magneto-plasmonic routers and magneto-plasmonic disk modulators for various nanophotonic functionalities.
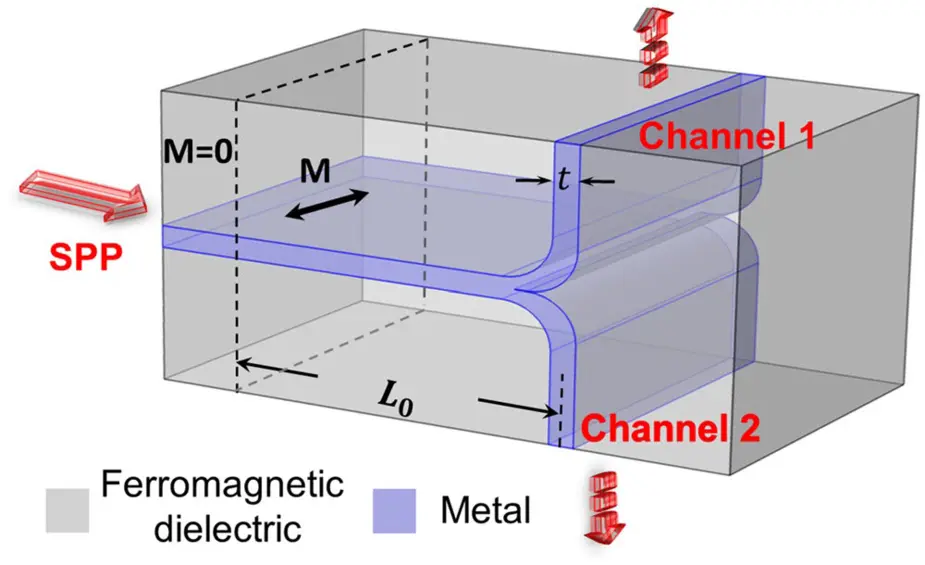
In a waveguide based on a metal film with a thickness exceeding the Skin depth and surrounded by a ferromagnetic dielectric an external magnetic field in the transverse direction can induce a significant spatial asymmetry of mode distribution of surface-plasmon-polaritons (SPP). Superposition of the odd and the even asymmetric modes over a certain distance leads to a concentration of the energy on one interface which is switched to the other interface by magnetic field reversal. The requested magnitude of magnetization is exponentially reduced with the increase of the metal film thickness. Based on this phenomenon, the group proposed a new type of waveguide-integrated magnetically controlled switchable plasmonic routers. A configuration of such nanodevice is shown in Fig. 1 consisting of a T-shaped metallic waveguide surrounded by a ferromagnetic dielectric under an external magnetic field inducing a magnetization M. In Fig. 2 numerical results for the plasmon propagation by solving the Maxwell equation show channel switching by the magnetic field reversal with a 99-%-high contrast within the optical bandwidth of tens of THz [1]. Here g is the gyration g=χM, χ is the magneto-optical susceptibility and g0 is a characteristic gyration requested to induce a significant mode asymmetry. Magnetic field revisal by integrated electronic circuits can be realized with a repetition rate in the GHz region. Note that up to now there exist only few papers reporting the realization of switchable plasmonic routers based on branched silver nanowires controlled by the polarization of the input light.
In a second paper [2] the group proposed and studied a novel type of ultra-small plasmonic modulator based on a metal-isolator-metal waveguide and a side-coupled magneto-optical disk controlled by an external magnetic field (see Fig.3). The wavenumber change and the transmission of surface-plasmon-polaritons (SPPs) can be tuned by altering the magnetic field and reversible on/off switching of the running SPP modes by a reversal of the direction of the external magnetic field is demonstrated. Resonant enhancement of the magneto-plasmonic modulation by more than 200 times leads to a modulation contrast ratio more than 90% keeping a moderate insertion loss within an optical bandwidth of hundreds of GHz. Numerical simulations by the solution of Maxwell's equations confirm the predictions by the derived analytical formulas of a high-contrast magneto-plasmonic modulation. Fig. 4 shows the distribution of the magnetic field components of the SPPs at a gyration g=0.03 and g=-0.03, respectively. As seen by changing the direction of the external magnetic field, the transmission of the SPPs is switched from an off to an on state via the changed interference pattern in the waveguide.
Original publication:
Kum-Song Ho, Song-Jin Im, Ji-Song Pae, Chol-Song Ri, Yong-Ha Han and Joachim Herrmann
"Switchable plasmonic routers controlled by external magnetic fields by using magneto-plasmonic waveguides"
[1]Scientific Reports (2018) 8:10584 /DOI:10.1038/s41598.018.28567.8
Ji-Song Pae, Song-Jin IM, Kum-Song Ho, Chol-Song Ri, Sok-Bong Ro and Joachim Herrmann
"Ultracompact high-contrast magneto-optical disk resonator side-coupled to a plasmonic waveguide and switchable by an external magnetic field".
[2] Phys. Rev. B 98, 041406 (R) (2018).
Contact:
Dr. Joachim Herrmann
Tel.: 030 6392 1278