Latest news from Analytic City Adlershof

Exploring the Hidden Secrets of Inorganic Particles and Formulations through X-ray Insights
LUM GmbH offers new solutions with the Gravity Separation & Particle Analyser LUMiReader® X-Ray 440:
The new Gravity Separation & Particle Analyzer LUMiReader® X-Ray 440 now complements the product range of LUM GmbH. Based on the patented and decades-proven STEP-Technology® (Space and Time resolved Extinction…

BAM and University of Birmingham extend strategic research partnership
Thematische Schwerpunkte sind Energie, Additive Fertigung, Umwelt- und Lebenswissenschaften sowie Chemie und Materialien:
The Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing (BAM) and the University of Birmingham (UoB) are continuing their successful strategic research partnership. The Memorandum of Understanding (MoU), originally…

Time matters
Which research questions call for short measurement times, and which analyses require longer ones? A brief journey through time and the Adlershof campus:
Watching molecular and atomic building blocks while they work? This is made possible by operando studies. Such deep insights at an atomic resolution are facilitated by BESSY II, a research facility operated by the…
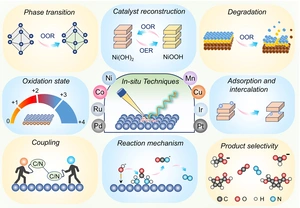
Electrocatalysis with dual functionality – an overview
Synchrotron sources provide insights into complex reactions and can thus help in the development of hybrid electrolysers:
Hybrid electrocatalysts can produce green hydrogen, for example, and valuable organic compounds simultaneously. This promises economically viable applications. However, the complex catalytic reactions involved in…

Phosphorous chains – a 1D material with 1D electronic properties
One-dimensional electronic properties of a material were experimentally demonstrated for the first time at BESSY II:
For the first time, a team at BESSY II has succeeded in demonstrating the one-dimensional electronic properties of a material through a highly refined experimental process. The samples consisted of short chains of…
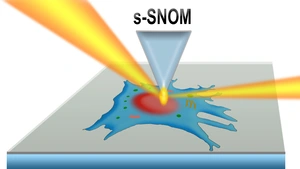
What vibrating molecules might reveal about cell biology
At BESSY II, molecular vibrations in tiny biological samples can now be detected and analysed:
Infrared vibrational spectroscopy at BESSY II can be used to create high-resolution maps of molecules inside live cells and cell organelles in native aqueous environment, according to a new study by a team from HZB…

Perovskite solar cells from Germany are competing with China’s PV technology
Kevin J. Prince and Siddhartha Garud receive HZB 2025 Technology Transfer Award:
Photovoltaics is the leading technology in the transition to clean energy. However, traditional silicon-based solar technology has reached its efficiency limit. Therefore, a HZB-team has developed a perovskite-based…
HU research team develops new quantum sensor
Defects in the crystal lattice of materials can be measured in real time and with unprecedented precision:
From computer chips to quantum dots—technological platforms such as these were only made possible thanks to a detailed understanding of the used solid-state materials, such as silicon or more complex semiconductor…

PFAS filter from a ball mill
BAM team develops environmentally friendly material that could help remove these ‘forever chemicals’:
PFAS are fluorinated compounds found in many everyday products, such as outdoor clothing and cookware like Teflon pans. This is because PFAS are durable, heat-resistant and dirt-repellent. Their stability is precisely…
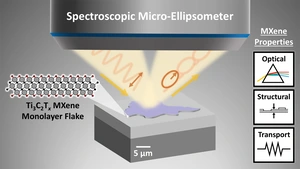
Novel technique shines light on next-gen nanomaterials
Team from HZB and Hebrew University uses spectroscopic microellipsometry to investigate how MXenes truly work:
Researchers have for the first time measured the true properties of individual MXene flakes — an exciting new nanomaterial with potential for better batteries, flexible electronics, and clean energy devices. By using…

PicoQuant Invests in FluoBrick Solutions to Simplify Access to Single Molecule Research
Partnering to make advanced fluorescence techniques intuitive, affordable, and accessible:
PicoQuant GmbH has invested in FluoBrick Solutions GmbH, a Berlin-based start-up dedicated to lowering the barriers to single-molecule techniques such as Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy (FCS) and Förster…
BAM develops innovative measurement methods for safe rechargeable batteries
EU project on sustainable batteries combines several independent measurement methods for analysis under realistic operating conditions:
The Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing (BAM) is participating in a major European project to develop new measurement methods for sustainable battery materials. The aim is to fundamentally improve the…

HZB team investigates lithium-sulphur batteries in real-time
Findings are helpful to design compact Li-S batteries with a high energy density:
Using a non-destructive method, a team at HZB investigated practical lithium-sulphur pouch cells with lean electrolyte for the first time. With operando neutron tomography, they could visualise in real-time how the…
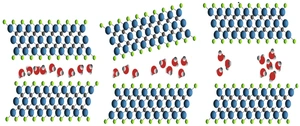
MXene as a frame for 2D water films shows new properties
Research team investigates phase changes of confined water at BESSY II:
An international team led by Dr. Tristan Petit and Prof. Yury Gogotsi has investigated MXene with confined water and ions at BESSY II. In the MXene samples, a transition between localised ice clusters to…

BAM researches more sustainable titanium production from industrial residues in EU project
LTB Lasertechnik Berlin in Adlershof provides support with real-time analysis method:
Titanium metal is a critical raw material that the EU imports largely from Kazakhstan, Russia, and China. The Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing (BAM) is part of a large EU consortium that aims to…